Gluten intolerance is a silent disruptor of many bodily functions, and the signs aren’t always obvious. For some, consuming gluten may result in immediate discomfort, while for others, the effects might be subtle yet impactful over time. This article will explore 9 clear signs that your body might be suffering from gluten, along with practical advice for managing gluten sensitivity.
1. Trouble Conceiving: Gluten Could Be the Hidden Culprit
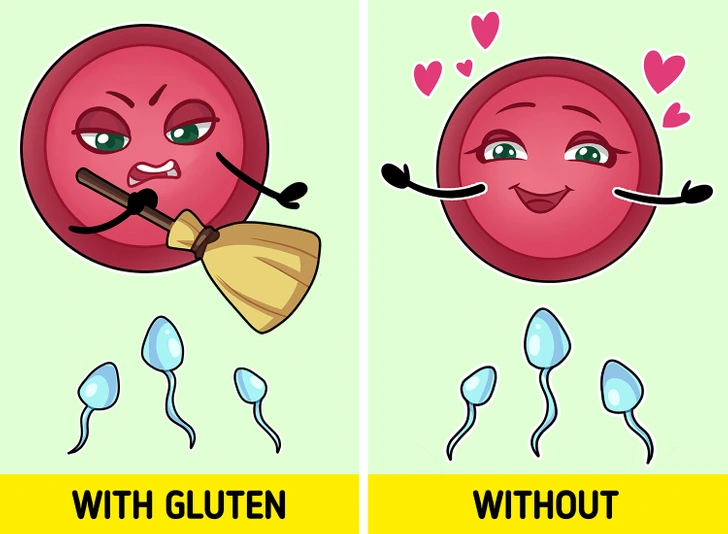
Struggling to conceive? It’s a lesser-known fact that gluten intolerance can sometimes be the underlying cause of infertility. Women dealing with unexplained fertility issues may not immediately connect their condition to gluten. However, research suggests that gluten intolerance can disrupt reproductive health, potentially leading to infertility or even miscarriage. If you’ve been having difficulty conceiving and haven’t found an explanation, it might be time to discuss gluten sensitivity with your doctor.
2. Unexplained Weight Fluctuations: Gaining or Losing Weight Without a Cause
Experiencing unexpected weight loss or gain? Gluten intolerance could be messing with your metabolism. This can happen due to an inflammatory response that occurs when gluten is consumed, which disrupts how your body absorbs nutrients. If these weight changes occur without a change in diet or lifestyle, gluten might be playing a bigger role in your health than you realize.
3. Digestive Issues: The Gut’s Struggle with Gluten
One of the most common ways gluten intolerance manifests is through digestive problems. Symptoms like bloating, gas, diarrhea, and abdominal pain may arise soon after consuming gluten. While these signs can easily be mistaken for other conditions, such as Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), the real issue may lie in gluten sensitivity. Many who switch to a gluten-free diet report a significant improvement in their gastrointestinal health.
4. Mental Fog and Migraines: Gluten’s Effect on Your Brain
Gluten can also impact your central nervous system, leading to problems such as brain fog, difficulty concentrating, and even depression or anxiety. Some individuals report feeling mentally sluggish or easily irritable after eating foods with gluten. Additionally, migraines are another common symptom for those with gluten intolerance. If you frequently experience headaches after meals, gluten could be a trigger.
5. ADHD Symptoms: A Surprising Link to Gluten Sensitivity
For those with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), gluten might exacerbate symptoms. Both children and adults with ADHD who follow a gluten-free diet have reported improvements in focus and self-control. Although more research is needed, there’s a strong indication that gluten sensitivity could be linked to cognitive and behavioral issues like ADHD.
6. Skin and Nail Problems: Gluten’s Impact on Your Appearance
Does your skin often break out into rashes, or do your nails seem unusually brittle? Skin conditions like keratosis pilaris (commonly known as “chicken skin”) and herpetiform dermatitis can both be symptoms of gluten intolerance. These conditions often result in red, itchy rashes or bumps, particularly on the arms, face, and torso. Brittle nails and other nail disorders can also occur due to poor nutrient absorption in gluten-sensitive individuals.
7. Oral Health Deterioration: Your Mouth May Be Signaling Gluten Issues
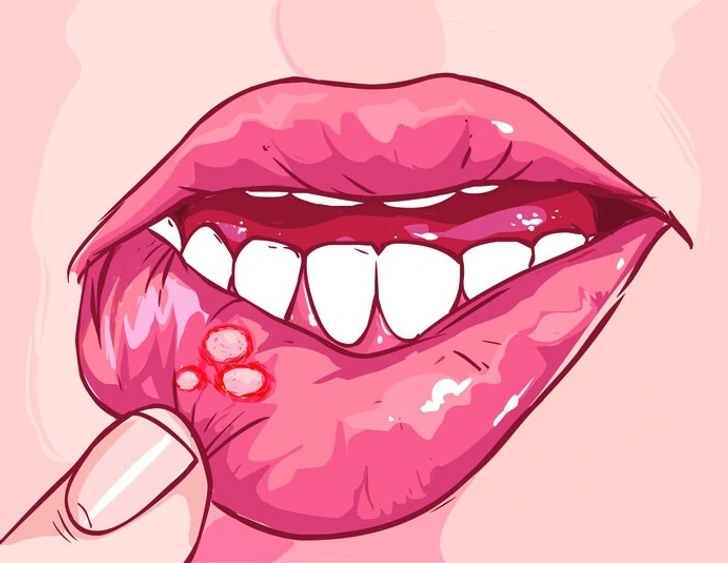

If you’re noticing increased cavities, sensitivity, or ulcers in your mouth despite good dental hygiene, gluten may be interfering with your oral health. Gluten sensitivity can hinder your body’s ability to absorb essential minerals like calcium, leading to weakened tooth enamel, cavities, and other oral issues. If you take good care of your teeth but continue to experience these problems, it might be time to evaluate your gluten intake.
8. Iron Deficiency Anemia: Gluten Blocking Nutrient Absorption
Have you been diagnosed with iron deficiency anemia without an obvious cause? Gluten intolerance can impair the absorption of iron in the intestines, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, dizziness, and pale skin. If you’ve been struggling with low iron levels and aren’t sure why, gluten may be at the root of the problem.
9. “Gluten Face”: Puffy, Red, and Flushed Skin
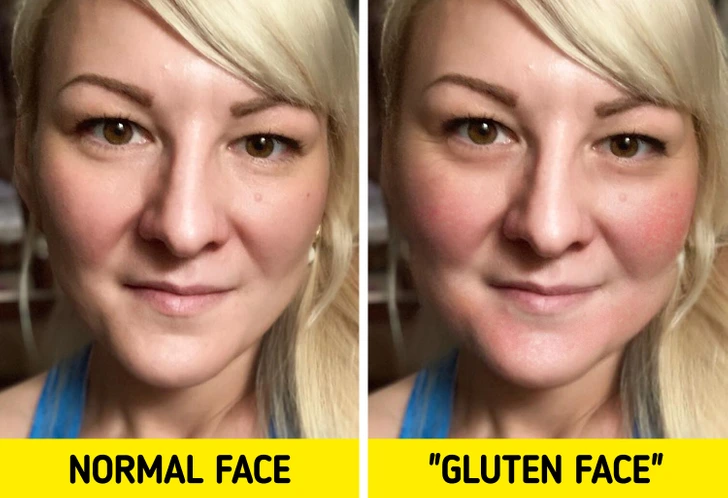

Have you noticed changes in your facial complexion, such as puffy red cheeks or dark spots around your chin? This condition, sometimes referred to as “gluten face,” is another common symptom of gluten intolerance. People with gluten sensitivity often experience facial flushing or redness after consuming gluten, which could be linked to changes in blood pressure or allergic reactions.
How to Identify and Manage Gluten Sensitivity
Managing gluten sensitivity requires both awareness and a proactive approach. If you suspect you’re suffering from gluten intolerance, here are some steps to take:
- Get Tested: The first step is to consult your healthcare provider for testing. A blood test can check for specific antibodies related to Celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. Keep in mind that you’ll need to consume gluten prior to the test for accurate results.
- Eliminate Gluten from Your Diet: If you test positive or choose to go gluten-free, you’ll need to avoid foods containing wheat, rye, barley, and other gluten-containing grains. Common sources include bread, pasta, and baked goods, but gluten can also hide in less obvious foods like sauces and processed snacks.
- Opt for Gluten-Free Alternatives: Many grocery stores now offer gluten-free options for a wide range of products. Be sure to check food labels, as even small amounts of gluten can trigger symptoms.
Conclusion: Listen to Your Body’s Gluten Signals
Our bodies are complex, and gluten sensitivity can manifest in many different ways. From digestive issues to skin problems and even mood disturbances, gluten intolerance is more than just a dietary inconvenience—it can affect your overall health. If you suspect gluten might be the cause of your discomfort, listen to your body’s signals and consider eliminating it from your diet. Taking the right steps now can prevent long-term health complications and improve your quality of life.