In a world where medical diagnoses can often be complex and time-consuming, a groundbreaking discovery has emerged that could revolutionize the way we identify certain traits and conditions. Researchers have uncovered an optical illusion that may just hold the key to unlocking insights about a person’s neurodiversity, and the implications are nothing short of astounding.
This mind-bending brainteaser doesn’t just captivate the senses – it could also provide a window into an individual’s neurological makeup, potentially shedding light on the presence of autistic traits in a matter of seconds. By analyzing how a person’s pupils respond to this visual puzzle, experts believe they may be able to gather valuable clues about their cognitive processing and attention patterns.
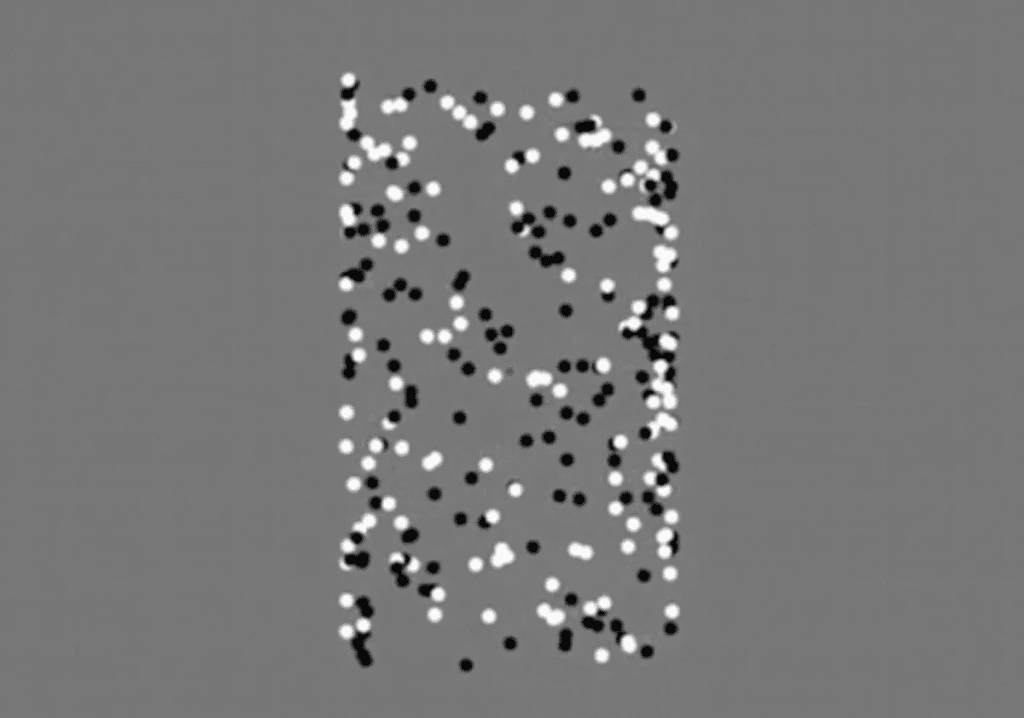

The optical illusion at the heart of this discovery is a deceptively simple one. It depicts a spinning cylinder made up of alternating black and white dots. For many people, this creates the illusion of a three-dimensional object rotating in space. However, the way in which individuals perceive and respond to this illusion can vary greatly.
A 2018 study published in the journal eLife found that the changes in a person’s pupil size as they view the optical illusion can correlate with the likelihood of them exhibiting autistic traits. Researchers discovered that those who tend to focus on the individual details of the illusion, flicking their gaze between the black and white dots, often score higher on tests measuring autistic tendencies.
The key to this phenomenon lies in the way the brain processes visual information. Individuals with autistic traits or tendencies are often known to have a heightened focus on details, rather than perceiving the “big picture.” This attention to detail is reflected in their pupil responses as they examine the optical illusion.
While this optical illusion cannot provide a full-fledged diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder (ASD), it could serve as a valuable screening tool. By identifying those who display the characteristic pupil oscillations associated with autistic traits, healthcare professionals can then recommend further evaluation and testing, potentially streamlining the diagnostic process.
The potential applications of this discovery are far-reaching. Not only could it lead to earlier identification of autistic traits, but it may also provide new insights into the neurodiversity of the human brain. Additionally, this optical illusion-based screening could have implications for a wide range of fields, from education to employment.
The current process of diagnosing autism spectrum disorder can be lengthy and complex, often requiring multiple evaluations and assessments. However, this optical illusion-based screening could significantly simplify and expedite the initial stages of the diagnostic process. By quickly identifying individuals who may be more likely to exhibit autistic traits, healthcare providers can then direct them towards the appropriate next steps, ultimately leading to more efficient and effective care.
For individuals and families affected by autism, the implications of this discovery are particularly profound. The ability to potentially identify autistic traits in a matter of seconds could provide a sense of empowerment and understanding, allowing them to seek out the necessary support and resources at an earlier stage. This could lead to improved outcomes and a better quality of life for those on the autism spectrum.
Beyond the realm of autism, this optical illusion-based screening could also have implications for our understanding of the human brain and its diverse cognitive processes. By examining how individuals respond to this visual puzzle, researchers may uncover valuable insights into the connections between attention, perception, and neurological function.
In the educational and workplace settings, this discovery could prove invaluable. By identifying individuals with autistic traits or tendencies, educators and employers can better tailor their approaches to accommodate diverse learning styles and cognitive preferences. This, in turn, could lead to enhanced performance, job satisfaction, and overall well-being for those with neurodivergent traits.
The discovery of an optical illusion that may hold the key to unlocking insights about autistic traits is a testament to the remarkable complexity and adaptability of the human brain. As researchers continue to explore the implications of this finding, the potential for improving lives and expanding our understanding of neurodiversity is truly exciting.