Chin hair in women is a common occurrence, yet it often sparks confusion and self-consciousness. While a few stray hairs might be easy to overlook, a sudden increase in facial hair growth can raise concerns about underlying health issues. Understanding the causes behind chin hair in women is crucial for managing it effectively. This article explores the factors that lead to chin hair growth and what they could reveal about your overall health.
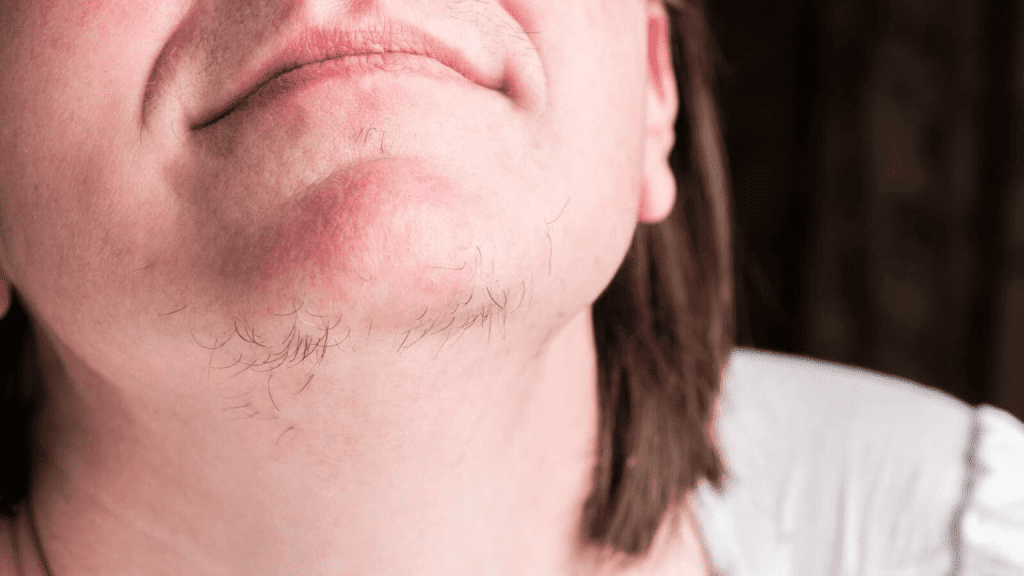

Understanding Chin Hair in Women: What’s Normal?
Every woman has some amount of facial hair, and it’s usually fine and light-colored. However, for some, chin hair can become coarser, darker, and more noticeable. This shift can happen due to a variety of factors, ranging from hormonal changes to genetic predispositions. Gaining insight into these causes is the first step towards effectively managing unwanted chin hair and addressing any underlying health concerns.
Hormonal Imbalances: The Role of Androgens
One of the primary drivers behind facial hair growth in women is a hormonal imbalance, particularly involving androgens. Androgens, often considered “male hormones,” are present in both men and women but in different amounts. An excess of these hormones in women can lead to hirsutism, a condition characterized by the growth of coarse hair in areas where men typically grow hair, such as the chin, upper lip, and chest.
Several factors can lead to an androgen imbalance, and one of the most common culprits is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). This condition is known for causing an overproduction of androgens, which not only leads to facial hair growth but also other symptoms like acne, irregular periods, and weight gain. Women experiencing an increase in chin hair, particularly alongside these symptoms, should consider consulting a healthcare provider to check for PCOS or other hormonal conditions.
Genetics: Why Family History Matters
Sometimes, the answer to chin hair growth can be as simple as genetics. If the women in your family have visible chin hair, it’s likely that you may experience it too. Genetics can influence both the amount and texture of hair you have, including where it grows on your body.
Certain ethnic backgrounds also tend to have more facial and body hair due to genetic differences. For instance, women of Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and South Asian descent are often more predisposed to noticeable facial hair than those from other backgrounds. If chin hair runs in your family, it’s likely a natural trait rather than a medical concern.
Medical Conditions Linked to Chin Hair Growth
While hormonal imbalances are a major cause of chin hair growth, there are also specific medical conditions that can contribute to increased facial hair in women. Here are a few key conditions to be aware of:
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
As previously mentioned, PCOS is one of the leading causes of hirsutism in women. This hormonal disorder leads to an excess of androgens, triggering hair growth on the chin and other areas. In addition to unwanted hair, women with PCOS often experience symptoms like irregular menstrual cycles, difficulty losing weight, and sometimes even infertility.
Adrenal Disorders
The adrenal glands are responsible for producing hormones, including androgens. Disorders such as Cushing’s syndrome can cause the adrenal glands to release high levels of cortisol and other hormones, leading to hirsutism. Women with adrenal disorders may notice an increase in chin hair and experience symptoms like unexplained weight gain, fatigue, and high blood pressure.
Thyroid Conditions
Both hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can influence hair growth patterns. The thyroid plays a central role in regulating metabolism, which in turn affects how the body produces and manages hair growth. Thyroid imbalances can lead to changes in hair texture, thickness, and distribution, including on the chin.
Aging and Menopause: Natural Hormonal Shifts
As women approach menopause, their bodies undergo significant hormonal changes, primarily involving a decrease in estrogen levels. This reduction in estrogen can cause a relative increase in androgens, which can lead to the development of new facial hair, particularly on the chin.
Aging itself can also contribute to increased hair growth in certain areas while causing thinning in others. For women experiencing these changes, chin hair is often a natural part of the aging process rather than a sign of a health issue.
Medications and Side Effects on Hair Growth
Certain medications can lead to unexpected side effects, including facial hair growth. Steroids, for instance, are known to promote hair growth in areas like the face, especially with prolonged use. Hormone-based treatments, such as certain birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy, can also affect hair growth. Additionally, some medications used for epilepsy and high blood pressure may contribute to hirsutism as a side effect.
If you’ve recently started a new medication and notice an increase in chin hair, it’s worth discussing this with your doctor to explore alternative options or manage the side effects.
Diagnosis and When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
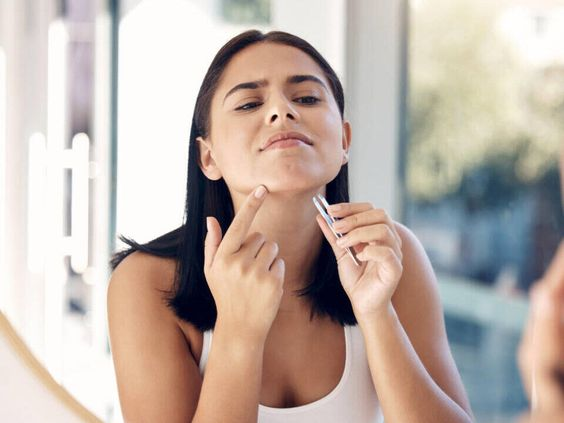

If you suddenly notice an increase in chin hair, especially if it’s accompanied by other symptoms like irregular periods, rapid weight gain, or severe acne, it’s essential to seek medical advice. Your healthcare provider can help determine if an underlying condition, such as PCOS or a thyroid disorder, is causing the hair growth. A physical exam, along with blood tests, can reveal whether hormonal imbalances are at play.
Identifying the cause of unwanted facial hair is the first step toward effective treatment. Medical intervention can include hormonal therapies, anti-androgen medications, or procedures like laser hair removal and electrolysis for more permanent results.
Treatment Options and Lifestyle Remedies
Once you understand the cause, there are several treatment options available. These can range from medical interventions to natural remedies depending on the severity of hair growth and your personal preferences.
- Hormonal Therapy: For cases related to hormonal imbalance, hormonal therapies or anti-androgen medications can help regulate hormone levels and reduce hair growth.
- Laser Hair Removal and Electrolysis: These cosmetic treatments offer longer-lasting hair removal options. Laser hair removal is effective for targeting darker, coarser hair, while electrolysis can provide permanent hair removal for lighter or finer hair types.
- Home Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments: For milder cases, natural remedies and lifestyle changes can help. Consuming a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and managing stress can all contribute to balanced hormone levels, which may help reduce facial hair growth over time.
Conclusion: Chin Hair is Often a Manageable Condition
Chin hair in women can be linked to a variety of causes, from genetics and hormonal changes to specific medical conditions. Understanding these factors can help you make informed choices about managing it effectively. While some chin hair may be normal, especially with age, a sudden increase in coarse or dark hair could signal an underlying issue that may require medical attention.
If excessive chin hair is causing you concern, don’t hesitate to seek guidance from a healthcare provider. With the right diagnosis and treatment plan, you can manage this condition and focus on feeling confident and comfortable in your skin.