In an era where digital streaming and smartphones dominate the media landscape, traditional radio might seem like a thing of the past. Yet, millions of people still tune in to AM and FM radio, especially in cars, rural areas, and during emergency broadcasts. Recently, a growing number of people have been pointing out the distinctions between FM and AM radio, raising awareness of how these two types of broadcasting differ. While the static noise of AM and the clearer sound of FM may be familiar to many, the underlying technical differences between the two can be surprising.
Let’s dive into what makes FM and AM radio unique and why understanding these differences can enhance your listening experience.

How Radio Works: The Basics
Before understanding the differences between FM and AM, it’s essential to grasp how radio broadcasting operates. Radio stations rely on carrier waves, which are electromagnetic waves used to transmit information. These waves have a fixed frequency (the number of times the wave oscillates per second) and amplitude (the height of the wave).
When a radio station broadcasts music, talk shows, or news, it encodes this content by modifying either the frequency or amplitude of the carrier wave. Your radio receiver picks up this modified wave, decodes the information, and converts it back into the sound you hear through your speakers.
AM Radio: What Is Amplitude Modulation?
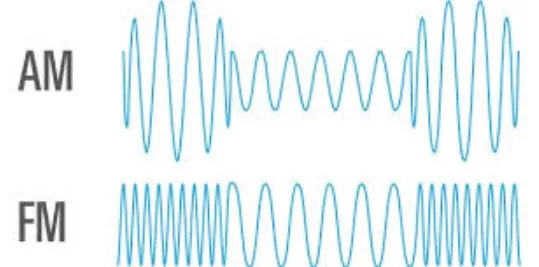
AM, or Amplitude Modulation, is one of the oldest forms of radio broadcasting. In AM radio, the amplitude of the carrier wave is modulated to carry the sound signal. This means that the height (or strength) of the wave fluctuates to represent the broadcasted content, while the frequency remains constant.
AM has some distinct advantages:
- Longer range: AM waves can travel long distances, especially at night when the atmosphere reflects them further. This allows AM stations to reach listeners in remote areas and penetrate buildings better than FM.
- Lower bandwidth requirement: AM radio uses less bandwidth, meaning more stations can broadcast on the AM spectrum.
However, AM radio also has several drawbacks:
- Susceptibility to interference: AM signals are easily affected by external sources such as electrical equipment, lightning, and even tall buildings. This can cause the familiar static or buzzing sound you hear when tuning into an AM station.
- Lower sound quality: AM radio has limited bandwidth, which results in lower fidelity. It’s suitable for talk shows and news but lacks the clarity required for music or high-quality audio broadcasts.
FM Radio: What Is Frequency Modulation?
FM, or Frequency Modulation, takes a different approach. In FM radio, it’s the frequency of the carrier wave that’s adjusted to encode the sound signal, while the amplitude remains constant. This method makes FM less susceptible to the types of interference that plague AM broadcasts.
Here’s why FM is favored for music and high-quality broadcasts:
- Superior sound quality: FM radio offers much clearer audio than AM because it has a larger bandwidth. This allows for better sound reproduction, making it the preferred choice for music stations.
- Less interference: Since FM waves aren’t affected as much by changes in amplitude, they experience less static and noise, especially in urban areas with lots of electrical interference.
Despite these advantages, FM has some limitations:
- Shorter range: FM waves have shorter wavelengths, meaning they don’t travel as far as AM waves. FM broadcasts tend to be more localized, making them ideal for urban areas but less effective for rural listeners or long-distance transmissions.
- Line-of-sight transmission: FM signals require a direct path between the transmitter and receiver, which means they can be blocked by obstacles such as mountains or buildings.
The Key Differences Between FM and AM Radio
While both FM and AM use carrier waves to transmit audio, the way they modulate these waves creates significant differences in their performance. Here’s a quick comparison:

AM radio is more prone to static due to interference from other sources. Image Credits: Getty
- AM Modulation: Alters the amplitude of the wave to encode the sound. This allows for long-distance broadcasting but is more prone to interference and offers lower sound quality.
- FM Modulation: Adjusts the frequency of the wave, resulting in superior sound quality with less interference, but a shorter broadcast range.
Why AM Radio Still Has a Place
Even though FM generally offers better sound quality, AM radio continues to play a crucial role, particularly in regions that need extensive coverage. AM’s ability to broadcast over long distances makes it invaluable for reaching remote areas and for emergency communications. In fact, many government and emergency alert systems rely on AM broadcasts due to their wide-reaching capabilities.

In rural areas or during natural disasters, when other communication systems may fail, AM radio is often the most reliable way to distribute information.
Why FM Radio Dominates the Airwaves
On the other hand, FM radio has become the dominant form of broadcasting in cities and urban areas due to its clearer sound and ability to broadcast music in high fidelity. Whether you’re driving through the city or relaxing at home, FM stations deliver the best audio experience, especially for entertainment purposes.
While FM’s shorter range limits its coverage, many radio stations use a network of repeaters or transmitters to cover larger areas, ensuring that listeners can enjoy quality sound without interference.
Understanding the Practical Uses of FM and AM Radio
The differences between AM and FM aren’t just technical—they impact how we use these radio technologies in everyday life. FM’s sound clarity makes it the go-to for music lovers, while AM’s wide coverage ensures that no one is left without access to important broadcasts, especially in rural or disaster-prone areas.
Conclusion
The distinction between FM and AM radio may seem simple, but it’s rooted in complex technologies that influence how we listen and what we hear. FM’s frequency modulation provides superior sound quality, making it ideal for entertainment and music. Meanwhile, AM’s amplitude modulation gives it the ability to cover vast distances, ensuring reliable communication even in the most remote locations.
As technology advances, traditional radio continues to play an essential role in our lives, providing both entertainment and critical information. Understanding the key differences between FM and AM radio allows us to appreciate their unique strengths and practical applications. Whether you’re tuning into your favorite FM music station or relying on AM for emergency updates, radio remains a timeless and valuable tool in the digital age.


